

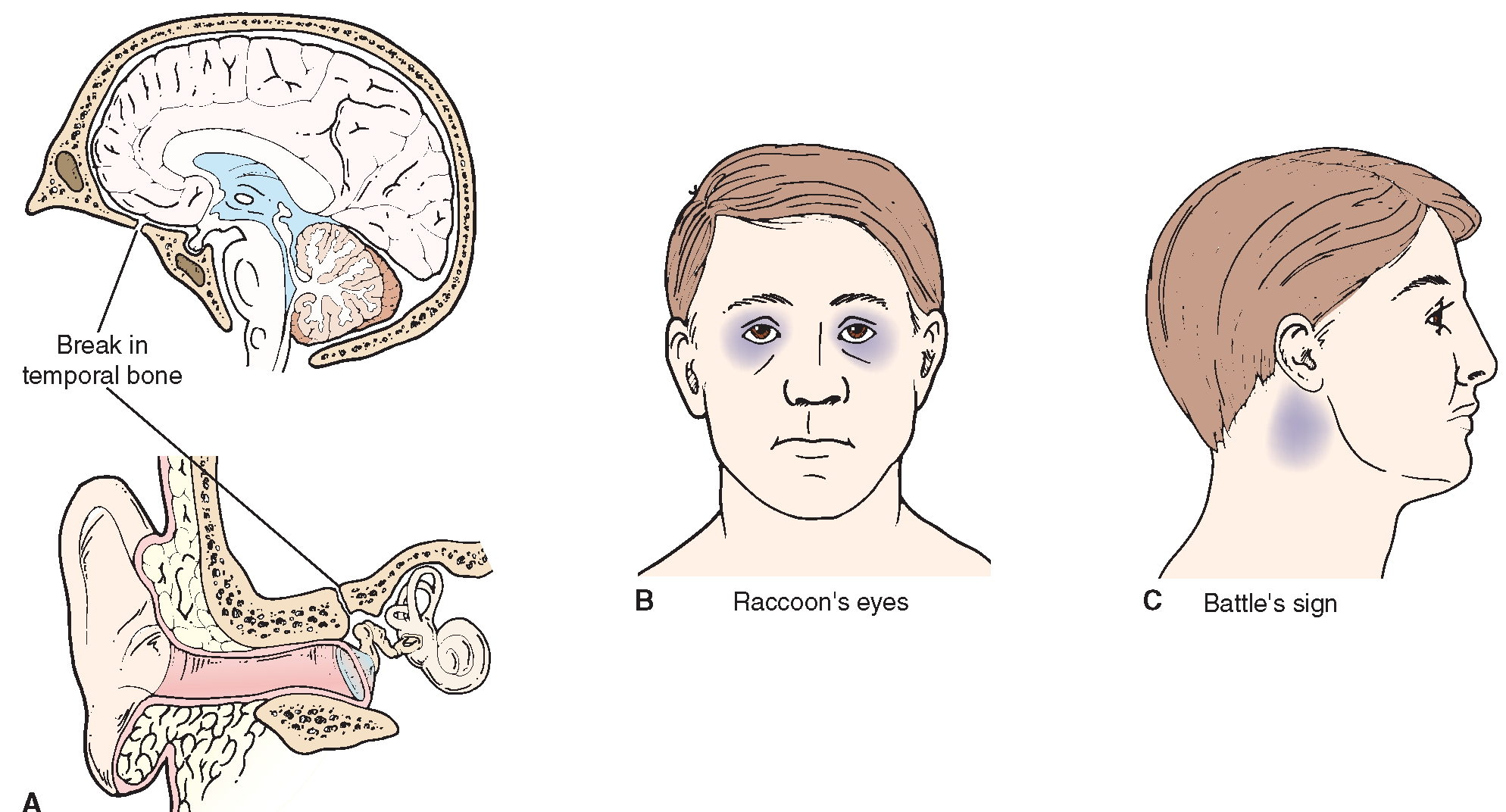
Among the air cells, the larger and irregular ones at the superior and anterior parts contain air, whereas those at the inferior part shrink in size, whereas the smaller ones near the apex contain marrow. Mastoid air cells do not develop until after birth, with about 90% of them being formed by the age of 6 and the remaining 10% occurring up until age 18.īimastoid skulls have the smallest diameter.Ĭellular mastoidal (mastoid air cells) are pneumatized portions of the mastoids that range in size and extent. Pneumatic bones are not found in the mastoid.Ī mastoid antrum is located in the temporal bone's petrous part. It is located in the upper part of the mastoid, this air-filled space measures 9mm high, 14mm wide, and 7mm deep. Anatomy, functional anatomy, and the clinical relevance of one of the projections, the mastoid process will be discussed below.Īn air space situated in the petrous portion of the temporal bone that is connected posteriorly with the mastoid cells and anteriorly with the middle ear recess is known as the mastoid antrum (aditus to mastoid antrum). In addition, it has air-filled spaces known as mastoid air cells. This is where many muscles of the head are attached. Just behind the ear, the mastoid process is easily palpable. The mastoid bone is a complex bone that, among other reasons, features a prominent bulge called the mastoid process. The temporal bone is one of the bones of the skull. Several projections are present on the interior surface, which are responsible for attaching many structures of the neck and face. The skull is made up of numerous small bones attached by fibrous joints.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
